When you’re starting to choose lighting for your home, it can be tough to know where to begin, even if you’re certain of the style you’re looking to create in your home. With so many different lighting options available, and lots of variables between the different types of bulbs, it can be pretty mind blowing. Through this post, we’ll take you through the different categories of lighting that you need in a room, and the types of fixtures that you can use for each category. From there, we’ll cover the important issue of light bulbs, since they’re pretty complex, and understanding how they work makes buying them much simpler.
We’ve written this post with absolute beginners to lighting in mind – those who are setting out living on their own for the first time, new home owners, and those who have previously ‘made do’ but are now ready to create a stylish home that they can be proud of.

What different types of lighting are there?
Where once we would have relied solely on the ceiling light to provide all the light in a room, today designers and lighting experts recommend having a range of different lighting available in a room – with at least one from each lighting category, to allow for optimal amounts of light for all the types of activities that may take place in the room. The main categories are ambient lighting, task lighting, and accent lighting.
As an example, in a bedroom:
- Ambient lighting allows for getting dressed and moving around
- Task lighting would allow for reading or for applying makeup
- Accent lighting may be used to illuminate wall accessories, behind a TV or an aspect of the room’s design
Ambient lighting
Ambient light completely fills the room with light, and allows you to use the room as if it is daytime. It is often provided by the ceiling light in the centre of the room, but there are other types of lighting that can contribute to ambient indoor lighting.
- Ceiling lighting fixtures which can include chandeliers, downlights, pendants, spotlights, track lights and batten lights
- Wall lighting fixtures such as picture lights, uplights, ceramic lights and flush wall lights
- Lamps of all types, including floor lamps, table and desk lamps
It may be the case that producing the optimal amount of lighting requires a number of lights to be used at the same time.
Task lighting
Task lighting does exactly what it sounds like – it produces light for specific purposes. This could be for reading, cooking or for studying. Task lighting can be provided by a range of lights, including:
- Downlights and pendants
- LED cabinet lights
- Lamps, including floor lamps, bedside table lamps, and desk lamps
The type of task lighting that may be required is likely to differ from room to room and between the type of activity that it is needed for. For example, a desk lamp that is only used with a PC, or under-counter lights in the kitchen may be able to be a fixed type, whereas for craft activities, a lamp with a moveable head may be desirable.
Accent lighting
Accent lighting can take many forms, but is primarily there to highlight an accessory such as artwork or an architectural feature. This can be provided by lots of different types of lights:
- Spot lights
- Uplights and downlights
- Arm lights
- LED strip lights
- Lamps of all types
Since accent lighting is there to highlight, then simpler light fixtures can help to keep the focus on the feature.

What type of lighting fixtures should I use?
The decision about which lighting fixtures you prefer is a personal one, and should be based on the type of look you are aiming to achieve in the room – but having at least one (if not more) of each type of lighting means that you’ll have the flexibility, and will be able to create the brightness that you need at any given time.
Ceiling lighting
Ceiling lighting is often the first lights that get chosen when moving into a new home. They tend to provide the general illumination in a room, but also add to the styling of the room.
While your personal preference, and the style and visual weight will ultimately guide your choice of ceiling lighting fixture, there are approximate calculations that you can use to narrow down the type of fixture that will work best in the space.
Working with the dimensions of your room in feet (rather than centimetres), add the number of feet in the width to the number in the length. The answer will give you the number of inches that your light fitting diameter should be. For example, if your room is 6 foot by 10 foot, the optimal size of light fitting would be 16 inches – which is about 40cm.
If you’re choosing statement lighting such as pendants that hang from the ceiling, the first thing to do is to get your tape measure out. It should go without saying, but you will need sufficient clearance underneath the fixture to avoid breakage and potential injuries. When hanging feature lighting from the ceiling, it is essential to have a minimum of two metres clearance between the floor and the bottom of the fixture (and if some members of the household are particularly tall, maybe a little more). If you’re hanging pendant lighting above dining tables, there should be at least 65cm between the table and the lighting fixture.
Wall lights
Wall lights can be used for all kinds of purposes – either to add to ambient lighting, as task lighting or as accent lighting – as well as providing a decorative accessory in a room with simpler styling. The function of the wall lights will influence the type of fixtures that you choose, while the style of the room will influence the type of wall lights that are chosen.
Where wall lights are used for effect, there may be a number of wall lights used – either paired, or in a series – or they may be positioned in an unusual spot. Using wall lights with colourful shades, and matching them with ceiling lighting can help to tie the overall look and feel of the room together, particularly where other accessories in the room coordinate.
Lamps
Whether you are choosing floor lamps, table lamps or desk lamps, as with wall lights, you’ll make your decision based on the size of the room, what category of lighting it is providing, and what activity the lamp will be illuminating.
Depending on their size, table lamps may contribute to the ambient light in a room, or may be purely used as task lighting – for example, for reading, or as a portable lamp that can be used for sewing or other types of crafts. Since more of us are using electronic devices for reading today (and are attached to our phones too), many styles of lamp now include USB charging points as part of their design. Where lamps are used for reading, dimmer switches are desirable – since this allows for better lighting throughout the day and night, when different levels of lighting are appropriate.
When choosing a table lamp:
- Be sure that the bottom of lamp shade is approximately at eye level when seated, so that the bulb doesn’t shine directly in your eyes
- Situate the lamp close enough to illuminate the task sufficiently
- If the room has people walking through it often, then ensure your lamp is stable, so to prevent it tipping over
- Ensure that the relative proportion of the lamp is appropriate – it should be no more than one and a half times the height of the item furniture that it sits on
When choosing a floor lamp:
- As with table lamps, ensure that the lower edge of the shade is at eye level when seated
- Avoid obstructing the view of décor such as artwork, as well as between seating locations
- The smaller the room, the smaller the lamp should be
- Keep safety first – if the floor lamp is likely to become a trip hazard (especially for children or elderly residents) it isn’t the right one

What type of light bulb do I need?
Once you’ve established the type of light fittings that you’re going to use in a room, and you’ve decided on the exact ones that you’re going to buy, you’ll need to choose your light bulb. Not all light fittings will have bulbs sent with them, and where they are, the bulb may not be to your preference. Choosing a light bulb isn’t always easy or straightforward either – since there are a number of variables that you’ll need to consider.
Choosing the right light bulb
If you’re replacing a bulb in an existing light fixture, the rule is to replace like with like – especially when it comes to the type of fitting. But the fitting isn’t the only thing you’ll need to consider. You’ll need to think about what the light is for (is it for ambient, accent or task lighting?), and what shape suits the fixture, as well as the cost both of the purchase, and in the longer term. Let’s take a look in more detail.
Fitting
While there are plenty of different types of light bulb fitting, when we’re looking at domestic light fittings, there are three main types that prevail: bayonet, screw cap, and pin and push-fit base bulbs. Generally, with these types of light fixtures, it should be easy to find a bulb that will suit.
When changing a bulb, you’ll need to find the same type of fitting for the replacement. Although adaptors are available, they should rarely be required, since different types of bulbs are so easily found today, especially from lighting specialists.
But establishing the fitting of the bulb is the easy part, since you don’t have to opt for the same colour or brightness – which is what we’ll come to next.
Function
As we’ve already determined, there are many different types of lighting fixtures, that can be used for different purposes. The function that the light fitting fulfils will determine the brightness, and the hue of the bulb that you choose.
Brightness
Newer types of bulbs use different amounts of watts to produce the same amount of brightness – and there are differences between types. Historically, light bulb manufacturers used the number of watts that were required to produce the amount of light to illustrate the brightness of a bulb.
Today, bulbs are much more efficient, and to produce the same amount of light as an old style incandescent 60 watt bulb, an LED bulb needs just 10 watts, while a halogen bulb requires around 42 watts. The differences in watts required for the same amount of light is the reason that light bulb manufacturers no longer use the measurement of watts to describe the brightness of a light bulb. So rather than measure the amount of power required, manufacturers now use Lumens to describe the levels of brightness that the bulb will provide. The higher the number, the brighter the light provided by the bulb.
Warmth
When choosing your light bulbs, you’ll also need to consider whether you want a cool toned, or a warm toned bulb. The decision will depend on several factors:
- What type of fixture you’re using the bulb in
- The space the light is being used in
- What activities the light will illuminate
- The time of day the room, and the light will be used
For rooms that require lighting levels that are near daylight, and that aren’t being used close to bedtime, then a cooler toned bulb can be used – bright white, or slightly blue-toned, will help to mimic natural daylight. Where being alert is not as desirable, such as for bedside table lamps, then warmer, yellow toned bulbs are preferable.
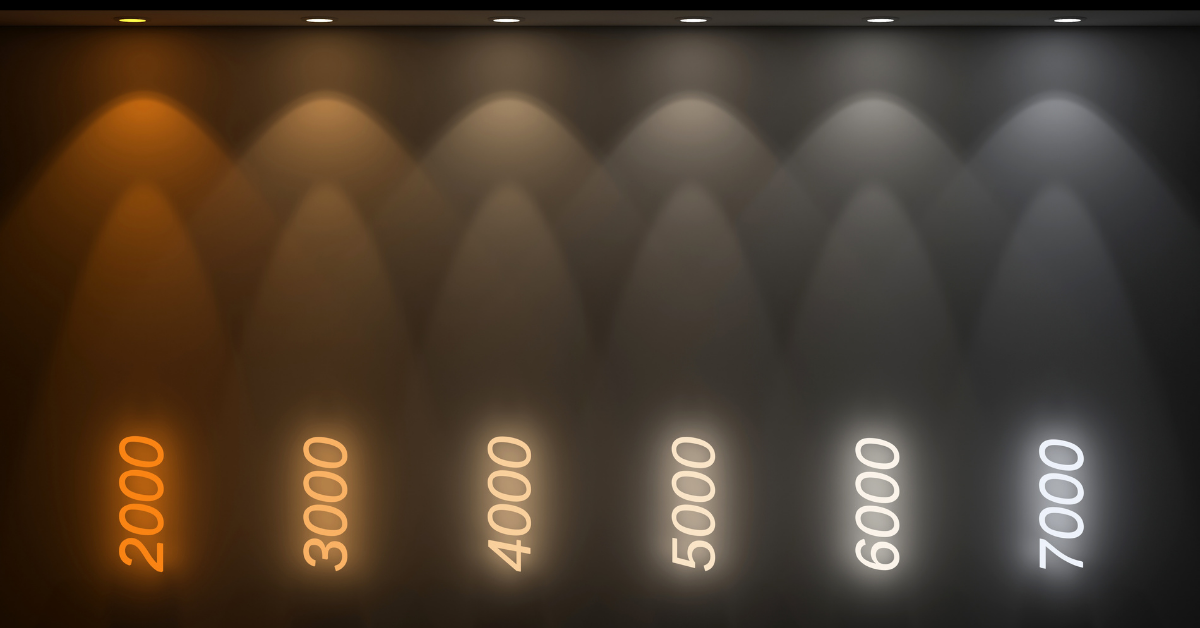
The measurement of bulb warmth is measured in Kelvins. The warmth of candle light is measured at approximately 1,500 Kelvin, while normal daylight (depending on whether it is a sunny or cloudy day) is measured at between 5,000 and 7,000 Kelvin. The higher the number on the Kelvin scale, the colder the light provided will appear, and cooler toned bulbs often appear to be brighter than warmer toned bulbs of the same Lumen measurement.
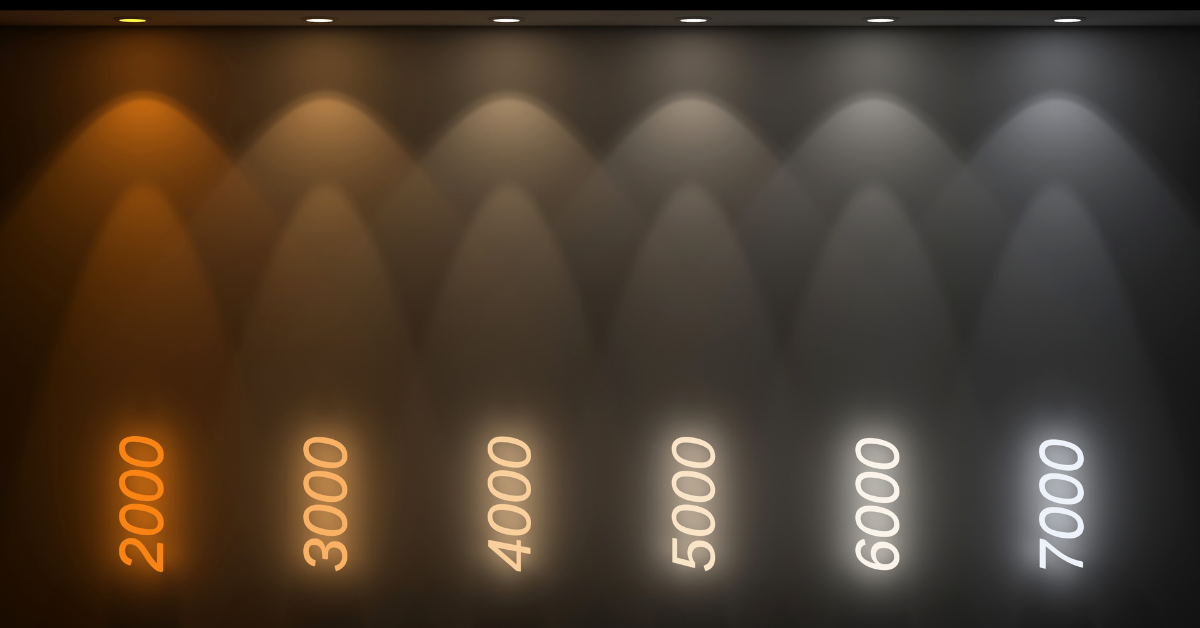

Choosing the bulb
Although watts are no longer used as a measurement of light bulb brightness, most bulb manufacturers will display both the Lumen measurement, and the equivalent in watts in an older style incandescent bulb, as well as the Kelvin measurement on the packaging. Not only that, but there will also usually be a description in words to describe the type of light – such as ‘warm white’. That means that when you’re in a store picking a light bulb, if you’re used to choosing bulbs based on watts, you’ll be able to see the numbers that you need, and the description will help if you’re not sure.
Format
Once you’ve decided on the colour, brightness and you know the fitting that you need, you can narrow down the shape that you want. There are an incredible array of different shaped bulbs, from traditional ‘bulb’ shapes, to candle, golf ball, pear shape, spiral and stick bulbs – and once you’ve established that you have the correct cap fitting (either screw or bayonet, for example) and the correct brightness, it is up to you. In many cases, if the bulb is hidden, the choice of bulb will be simply down to personal preference and it won’t matter. However, if your lighting fixture intentionally exposes the light bulb, then it may be better choose a style with a decorative filament, or that complements the design of the fixture.
Cost
While the general rule of buying the best quality you can afford definitely comes into play here – since a better quality bulb is likely to last longer too. The longer-term cost of running a bulb will also be relevant, especially if you are in your ‘forever home’. The initial cost of LED bulbs are higher than other types, but they are much more energy efficient, and can last for up to 25 years. Not only does this provide much more convenience – you won’t need to replace it as often – but the energy savings can add up dramatically. Savings can add up to more than £180 over the product’s lifetime, which makes it well worth the investment.
Final thoughts
We’ve covered the basics of lighting in this post, and yet we’ve barely touched on design. Understanding the basics of lighting is important though, and can help to guide your decisions when you’re designing, and shopping for the room of your dreams. Our key takeaways:
- Ensure you have a range of lighting in each room, with at least one light from each category of ambient, task and accent lighting
- Be careful to measure before making a purchase – having lighting that is in proportion to the room, and that allows sufficient clearance is essential
- Choosing the best bulb for the purpose should be done carefully, with the correct brightness and colour taken into consideration
Our range of lighting covers all the types of fixtures mentioned in this post, and we stock an extensive range of bulbs. If you are looking for a particular item, or need technical advice, please get in touch – our team of experts are happy to help.

Charles Barnett Managing Director
Charles started Lyco in 1995 with just 4 enthusiastic employees and has grown it considerably over the past 25 years. Charles is also the Managing Director of Lighting Direct and newly acquired Online Lighting. He now has a team of 50 lighting experts working on growing Lyco Group to be the UK leader in lighting for both businesses and homes. Away from the office he is a keen cyclist and is proud to have cycled 1017 miles from Lands End to John O’Groats to raise money for a new residential centre for adults with multiple learning difficulties.







 The
The 

 Finally the top selling LED light fitting which really is lighting the way to LED dominance in the lighting market is the
Finally the top selling LED light fitting which really is lighting the way to LED dominance in the lighting market is the 


